SaaS Business Model
Tradition software business model

- Setup to build and deliver a final product
- Long development and time-to-value (TTV)
- Focus on big one-time deals
- Siloed units with independent P&L responsibility
- Product dev & sales set direction
SaaS business model
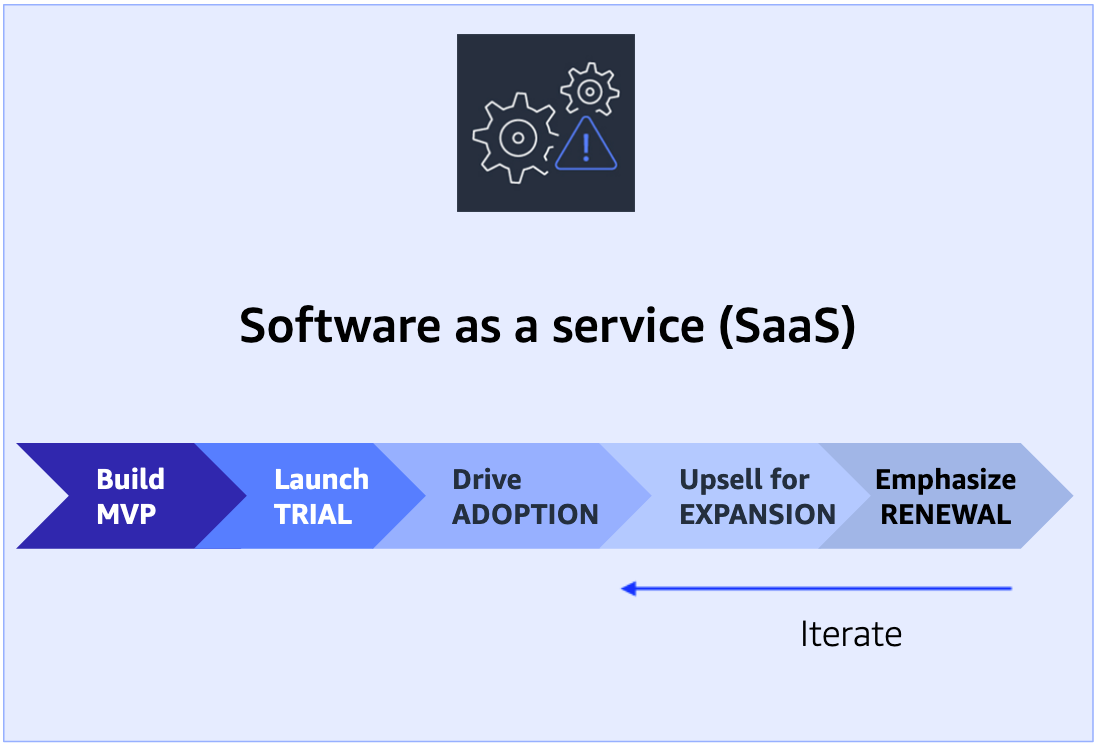
- Setup to deliver a service
- Launch with MVP, then expand, for better TTV
- Emphasis on customer retention and lifetime value (LTV)
- Integrated operations across units
- Broader cross-functional exec control
Adopting a service mindset
- Managing real-time relationship with customers
- Meeting SLAs at all times
- Customer experience drives business growth
- Focus changes from buyer to user
Organisation transformation
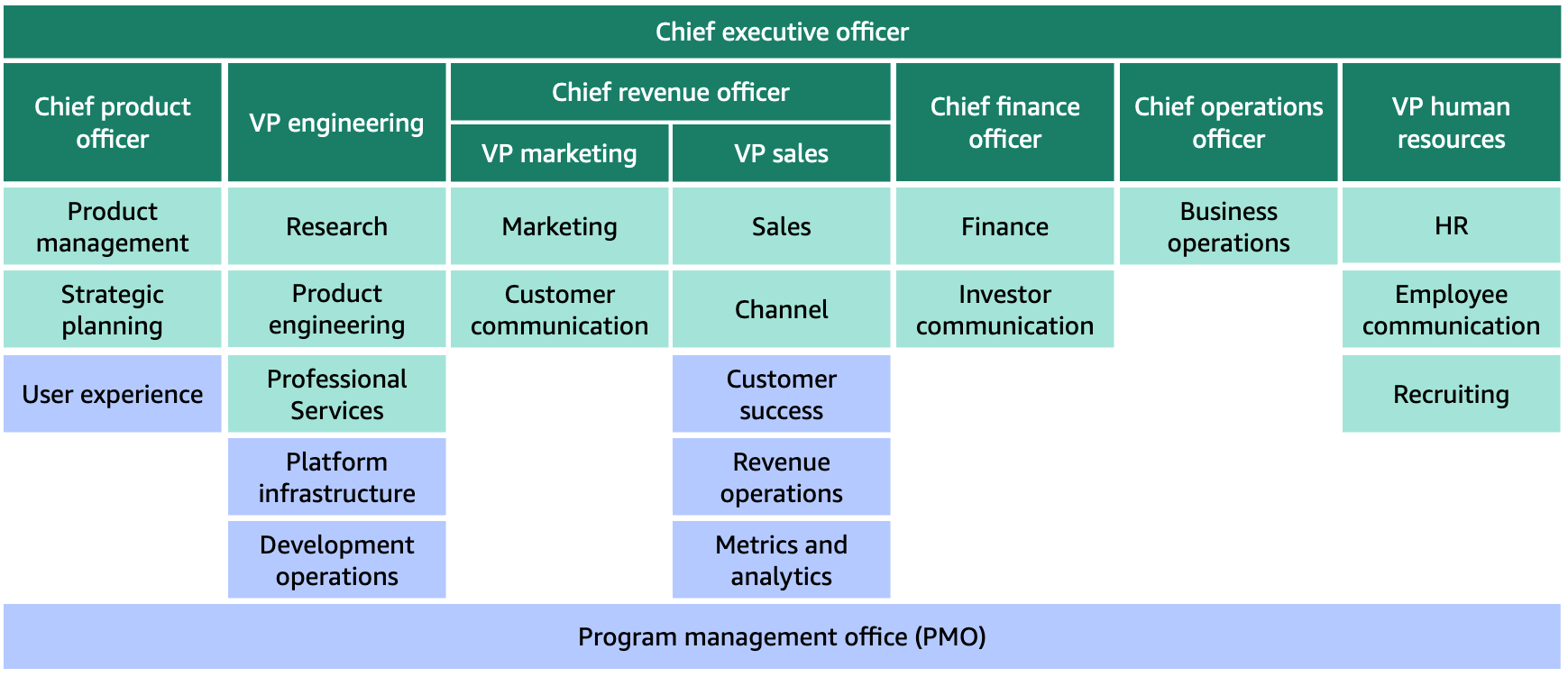
- New functions
- Project Management Office (PMO)
- Bridge between sales, customer success, and engineering
- Aligned with agile dev
- User experience added to product team
- Ops (Platform infrastructure, and DevOps) are part of engineering
- Sales extended
- Customer success
- Revenue operations
- Metrics and analytics
- Project Management Office (PMO)
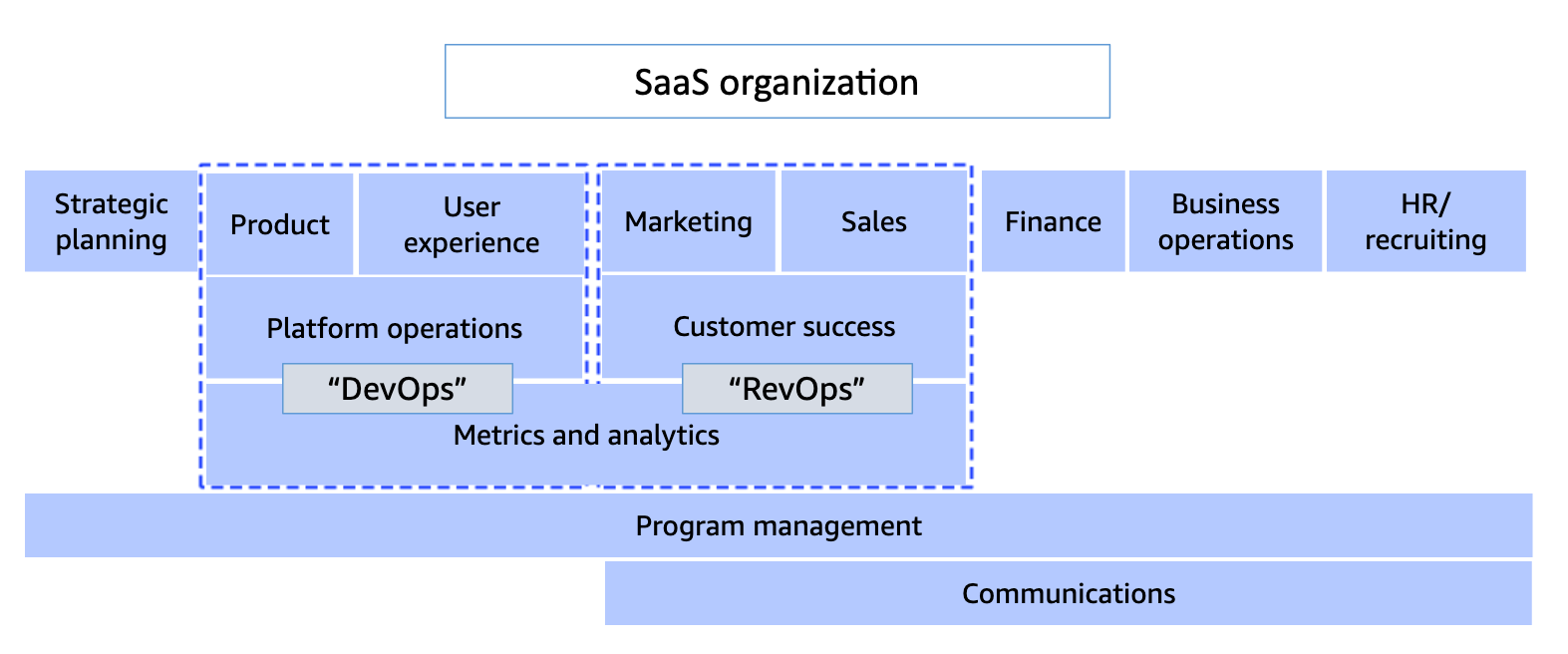
Operations
- Operating the service is the business
- Prioritise backend systems and metrics
- Create feedback loop for optimisation
- SaaS outages have direct business impact
- Achieve reliable delivery through DevOps
- Revenue operations track the customer journey
- Track gaps in the customer journey